Weed Watch: Velvetleaf
- // Weed Management
Velvetleaf
Once introduced to the U.S. as a source of fiber, velvetleaf is an erect summer annual that is now a problematic pest of row crops due to its highly competitive nature and allelopathic properties — or the ability of one plant to create biochemicals that can harm the germination, growth, survival and reproduction of other plants.1

Velvetleaf is present in the 48 continental U.S. states and categorized as noxious in four of those.1,2
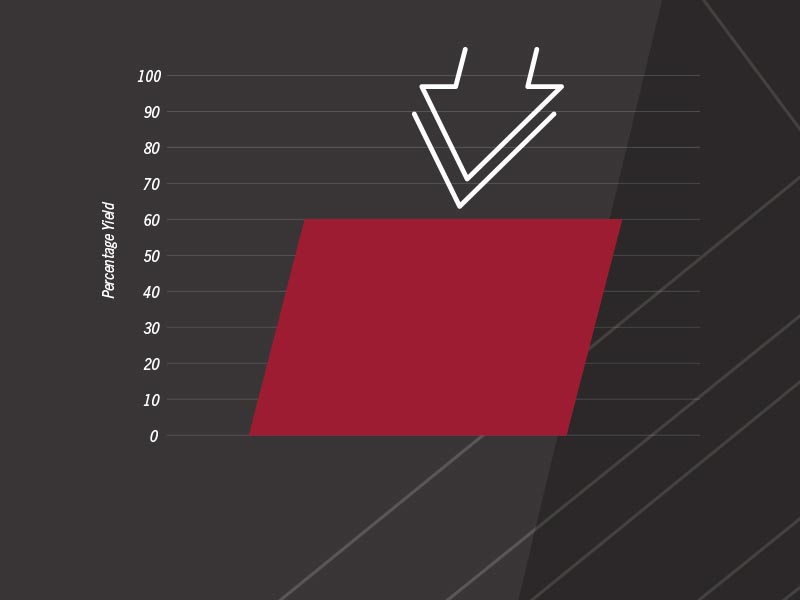
Reduced soybean yields of 25 to 40% with as few as 3-6 plants per square yard 3
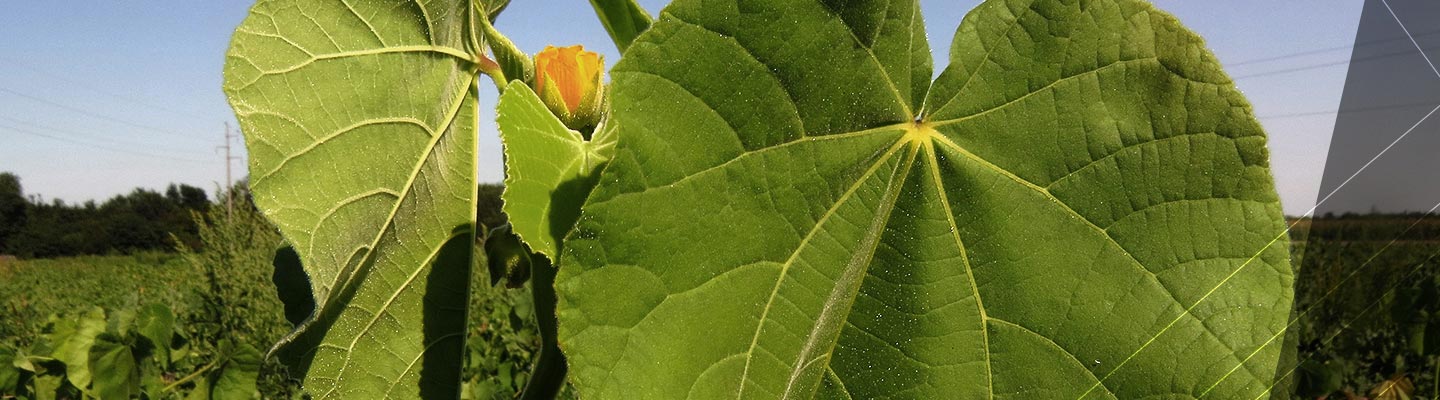
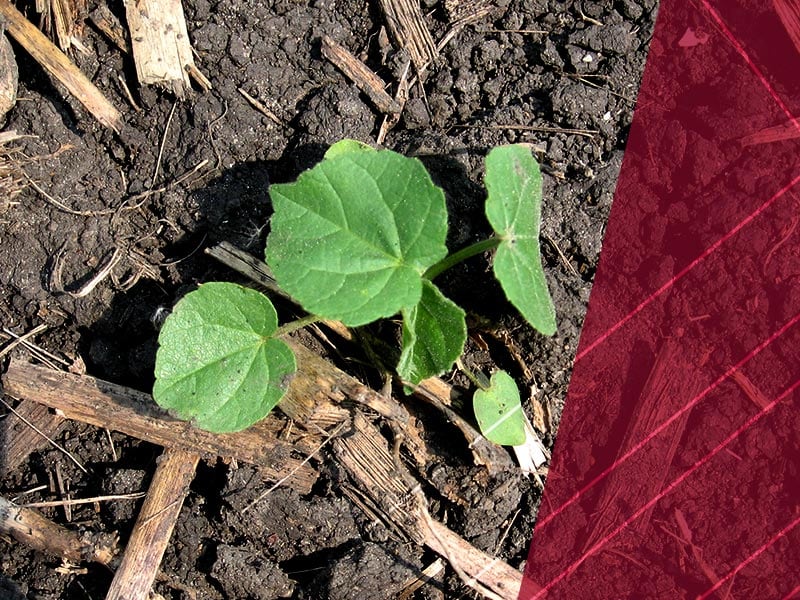
Young Plants
Velvetleaf is easily identifiable by its heart-shaped leaves that grow 2-6 inches long and wide and are covered with soft hairs on both sides.1,4
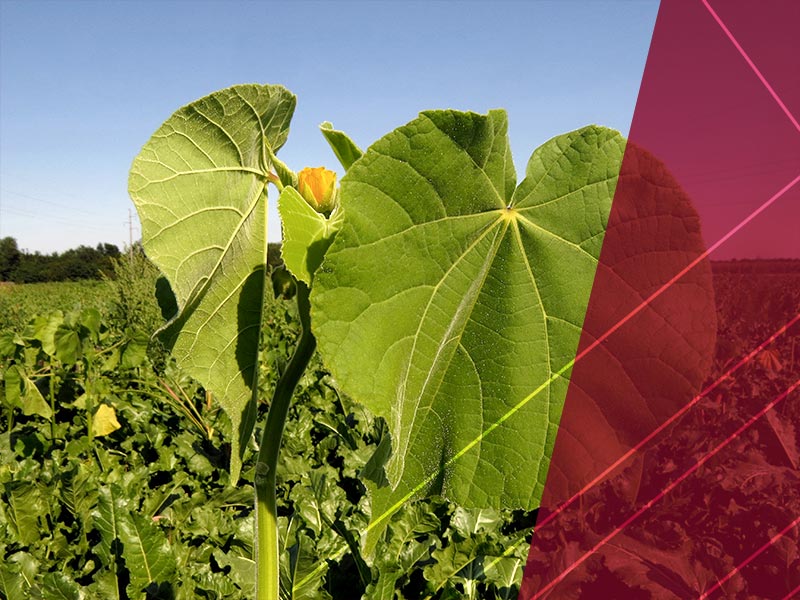
Mature Plants
Velvetleaf can grow to 8 feet but typically ranges between 2-4 feet in soybean fields.3
Seed Pain Points
Plants produce an average of 2,000-9,000 seeds, although one plant can produce up to 17,000 seeds — and seeds can persist in the soil for up to 60 years.1,5
Keys to Managing Velvetleaf 1, 3, 4
Rotate crops
to diversify herbicide programs and weed control strategies.
Start clean
with a burndown herbicide or tillage.
Apply a pre-emergence residual application,
using a residual product within 2 weeks before planting or prior to crop emergence.
Apply a postemergence application to target small weeds early,
before weeds grow taller than 4 inches.
Prevent Seed Production.
If weeds escape, use tillage or physically remove them before plants produce seed.
1 Bish, M., Bradley, K. University of Missouri Integrated Pest & Crop Management (May 28, 2015). Weed of the month: Velvetleaf. Retrieved from http://www.ipm.missouri.edu
2 United States Department of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service (Sep. 18, 2019). Abutilon theophrasti Medik. Vetvetleaf. Retrieved from http://www.plants.usda.org
3 Take Action. United States Soybean Board (Sep. 18, 2019). Velvetleaf. Retrieved from http://www.iwilltakeaction.com
4 University of Missouri Division of Plant Sciences (Sep. 19, 2019). Weed ID Guide, Velvetleaf. Retrieved from http://www.weedid.missouri.edu
5 King County (Sep. 18, 2019). Velvetleaf identification and control. Noxious Weed Control Program. Retrieved from http://www.kingcounty.gov
The System Proven to Fight the Toughest Weeds
Tough-to-control weeds like Velvetleaf can cause significant damage to your yield. See how Roundup Ready® Xtend Technology stacks up against competitors when controlling Velvetleaf and more.